Analog vs IP Camera: Which is Really Better?

Troubleshooting an IP Camera Not Detected by NVR

How to Reset an IP Camera Without a Reset Button


Analog and IP cameras are the two most prevalent kinds of surveillance cameras used for security and monitoring. Both offer distinct benefits and drawbacks, and the decision between the IP vs analog camera will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the user.
Image quality

The resolution of the recorded video is the primary factor that determines the distinction in an IP camera vs analog primarily lies. Analog cameras typically have a lower resolution, which results in less detailed and less clear images. IP cameras, on the other hand, have a higher resolution, which results in clearer and more detailed images.
Analog cameras generally have a resolution of standard definition (SD) or low-definition (LD), which is typically around 480p or 720x480 pixels. IP cameras, on the other hand, can have a resolution of high-definition (HD) or even ultra-high-definition (UHD), which is typically 1080p or 4K. The higher resolution of IP cameras allows for more accurate identification of individuals and objects in the video footage.
IP cameras often have features such as digital zoom, which allows for closer examination of specific areas of the video footage. Analog cameras typically do not have this feature.
Image transmission
The next step is the image transmission comparison of IP vs analog cameras. Analog cameras use a wired connection, typically a coaxial cable, to transmit video footage to a Digital Video Recorder (DVR) or monitor. The DVR or monitor then stores the footage for later viewing. This method of transmission is known as Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) and is limited by the distance between the camera and the DVR or monitor, as well as the number of cameras that can be connected to the DVR or monitor.
IP cameras use the Internet Protocol (IP) to transmit video footage over a network. This makes it possible for anybody with an internet connection to remotely view the video. IPs can be used with a Network Video Recorder (NVR) or a computer for recording and storage, or they can be accessed directly through an internet connection. The distance between the camera and the recording device is not limited as long as there is a network connection.
PoE capabilities
Comparing the power consumption of IP cameras vs analog ones, we did the following research. Analog cameras typically require less power than IP cameras, as they do not have as many advanced features and do not need to process and transmit digital data. They can be powered using a lower voltage standard known as PoE 802.3af (Power over Ethernet - Alternative A or B), which provides a maximum of 15.4 watts per port.
While IP cameras require more power as they have advanced features such as high-resolution video, digital processing, and network connectivity. They can be powered using a higher voltage standard known as PoE+ (Power over Ethernet Plus) or PoE++ (Power over Ethernet ++) which provides a maximum of 30 watts or 60 watts per port.
Wireless capabilities
Analog cameras, also known as CCTV cameras, typically use a wired connection to transmit the video signal to a monitor or a digital video recorder (DVR). They do not have built-in wireless capabilities and may require additional equipment such as a wireless video transmitter to connect to a wireless network.
Comparing the IP camera vs analog camera regarding the wireless capabilities, we noted that IP cameras have built-in wireless capabilities and can connect to a wireless network using various wireless standards such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and others. They can be accessed remotely via a mobile device, tablet, or computer using the internet. IP cameras can also be integrated into smart home systems and can be controlled and viewed remotely via an app or a web interface.
Security
The distinction in security capabilities between analog camera vs IP camera lies in their ability to provide secure video surveillance and the level of encryption used to protect the transmitted data.
Analog cameras typically use a wired connection to transmit the video signal to a monitor or a digital video recorder (DVR). The transmitted video signal is in an analog format, which can be intercepted and viewed by unauthorized individuals if the signal is not properly protected. Additionally, DVRs and monitors that receive the signal may not have built-in security features such as password protection or encryption.
To send video across a network, IP cameras employ digital technology, which enables more sophisticated security measures. They can use encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS to secure the video transmission and prevent unauthorized access. The cameras can also use password protection, two-factor authentication, and other security measures to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the video feed. Also, one important thing that should be mentioned in this comparison of IP cameras vs analog cameras, IP devices may be combined with components of other security systems, such as those for access control and intrusion detection, to provide a more all-encompassing security solution.
Features
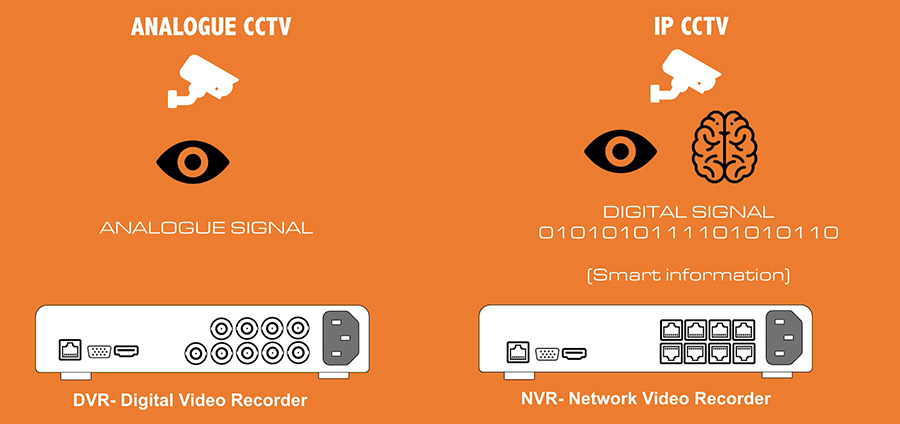
Analog cameras transmit video signals through a coaxial cable or twisted pair wire to a DVR or monitor. They use a standard definition resolution, typically around 480 or 540 lines, and are known for their simplicity and reliability. Analog cameras are also relatively inexpensive and easy to install, making them a popular choice for basic surveillance needs.
IP cameras transmit video signals over an internet protocol (IP) network. They use a high-definition resolution, typically around 720p or 1080p, and are known for their advanced features such as remote access, motion detection, and two-way audio. IP cameras are also more flexible, as they can be integrated with other devices and systems, such as access control and alarm systems.
The biggest difference between IP and analog camera is that IP units provide remote access to live and recorded video footage. This allows users to view their cameras remotely via a web browser or mobile app, making it possible to monitor their property from anywhere in the world.
Another advantage of IP cameras is their ability to be integrated with other devices and systems. For example, an IP unit can be integrated with an access control system to automatically unlock a door when a person is recognized. They can be integrated with alarm systems to trigger an alarm when motion is detected.
However, checking the price difference between analog and IP cameras, we noticed that IPs can be more expensive than analog ones and may require more technical expertise to set up and maintain. They also require a stable internet connection to function properly, which can be an issue in areas with poor internet connectivity.
Analog cameras, however, are a more cost-effective option for basic surveillance needs. They are also easier to install and maintain, as they do not require a network connection. Still, they don't have as many advanced features or as much flexibility as IP cameras, and the video quality is usually not as good.
Analog vs IP cameras: Conclusion
In conclusion, whether to choose an analog or IP camera will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the user. Analog cameras are a good choice for basic surveillance needs, while IP cameras are a better option for advanced features and flexibility. It's important to consider the cost, installation, and maintenance requirements, as well as the specific features and functionality needed when making a decision.


